xgboost
Mathias Riechel, Michael Rustler
Source:vignettes/prediction_xgboost.Rmd
prediction_xgboost.RmdInstall R Package
# Enable KWB-R universe
options(repos = c(
kwbr = 'https://kwb-r.r-universe.dev',
CRAN = 'https://cloud.r-project.org'))
# Install R package "dwc.wells"
install.packages('dwc.wells', dependencies = TRUE)Input Dataset
library(dwc.wells)
library(tidymodels)
#> ── Attaching packages ────────────────────────────────────── tidymodels 1.0.0 ──
#> ✔ broom 1.0.1 ✔ recipes 1.0.2
#> ✔ dials 1.0.0 ✔ rsample 1.1.0
#> ✔ dplyr 1.0.10 ✔ tibble 3.1.8
#> ✔ ggplot2 3.3.6 ✔ tidyr 1.2.1
#> ✔ infer 1.0.3 ✔ tune 1.0.1
#> ✔ modeldata 1.0.1 ✔ workflows 1.1.0
#> ✔ parsnip 1.0.2 ✔ workflowsets 1.0.0
#> ✔ purrr 0.3.5 ✔ yardstick 1.1.0
#> ── Conflicts ───────────────────────────────────────── tidymodels_conflicts() ──
#> ✖ purrr::discard() masks scales::discard()
#> ✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
#> ✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
#> ✖ recipes::step() masks stats::step()
#> • Dig deeper into tidy modeling with R at https://www.tmwr.org
df <- dwc.wells::model_data_reduced
str(df)
#> 'data.frame': 6308 obs. of 27 variables:
#> $ Qs_rel : num 100 97.8 75.1 78.5 52.2 ...
#> $ well_id : int 872166 872166 872166 872166 872166 872166 872166 872166 872166 872166 ...
#> $ well_age_years : num 0 23.2 29.3 29.5 35 ...
#> $ construction_year : num 1970 1970 1970 1970 1970 1970 1970 1970 1970 1970 ...
#> $ screen_material : Factor w/ 6 levels "3fe9575b","5bad81ff",..: 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 ...
#> $ diameter : num 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 ...
#> $ drilling_method : Factor w/ 6 levels "418861c3","484a778f",..: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ...
#> $ admissible_discharge : num 176 176 176 176 176 176 176 176 176 176 ...
#> $ operational_start.Qs : num 39.1 39.1 39.1 39.1 39.1 ...
#> $ aquifer_coverage : Factor w/ 5 levels "confined","edges confined",..: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ...
#> $ W_static.sd : num 0.766 0.766 0.766 0.766 0.766 ...
#> $ surface_water.distance: Factor w/ 8 levels "0-25","25-50",..: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ...
#> $ n_rehab : int 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 4 ...
#> $ time_since_rehab_years: num 0 0.0411 6.193 0.0794 5.5524 ...
#> $ volume_m3_d.mean : num 1203 1203 1203 1203 1203 ...
#> $ volume_m3_d.cv : num 1.29 1.29 1.29 1.29 1.29 ...
#> $ quality.EC : num 824 824 824 824 824 ...
#> $ quality.DO : num 0.235 0.235 0.235 0.235 0.235 0.235 0.235 0.235 0.235 0.235 ...
#> $ quality.Temp : num 11.7 11.7 11.7 11.7 11.7 11.7 11.7 11.7 11.7 11.7 ...
#> $ quality.pH : num 7.4 7.4 7.4 7.4 7.4 7.4 7.4 7.4 7.4 7.4 ...
#> $ quality.Redox : num 86 86 86 86 86 86 86 86 86 86 ...
#> $ quality.Fe_tot : num 1.9 1.9 1.9 1.9 1.9 1.9 1.9 1.9 1.9 1.9 ...
#> $ quality.Mn : num 0.24 0.24 0.24 0.24 0.24 0.24 0.24 0.24 0.24 0.24 ...
#> $ quality.NO3 : num 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 ...
#> $ quality.PO4 : num 0.966 0.966 0.966 0.966 0.966 ...
#> $ quality.SO4 : num 94 94 94 94 94 94 94 94 94 94 ...
#> $ quality.TSS : num 4.1 4.1 4.1 4.1 4.1 4.1 4.1 4.1 4.1 4.1 ...Resampling
resampling <- "random"
#resampling <- "by_well"
set.seed(1)
if (resampling == "random") {
# for regression
data_split <- rsample::initial_split(df %>% dplyr::select(-well_id),
prop = 0.8,
strata = Qs_rel)
df_training <- data_split %>% rsample::training()
df_test <- data_split %>% rsample::testing()
}
# version 2: splitting per well ids
if (resampling == "by_well") {
well_ids <- unique(df$well_id)
train_ids <- sample(well_ids, 0.8 * length(well_ids))
test_ids <- setdiff(well_ids, train_ids)
df_training <- df %>%
dplyr::filter(well_id %in% train_ids) %>%
dplyr::select(-well_id)
df_test <- df %>%
dplyr::filter(well_id %in% test_ids) %>%
dplyr::select(-well_id)
}
tibble::as_tibble(df_training)
#> # A tibble: 5,044 × 26
#> Qs_rel well_age_years const…¹ scree…² diame…³ drill…⁴ admis…⁵ opera…⁶ aquif…⁷
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <fct> <dbl> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <fct>
#> 1 31.5 42.3 1970 5bad81… 300 418861… 176 39.1 confin…
#> 2 20.7 44.2 1970 5bad81… 300 418861… 176 39.1 confin…
#> 3 16.3 47.9 1970 5bad81… 300 418861… 176 39.1 confin…
#> 4 22.4 47.9 1970 5bad81… 300 418861… 176 39.1 confin…
#> 5 25.6 25.8 1993 93242c… 393 418861… 93.5 44.7 unconf…
#> 6 19.0 16.2 1993 93242c… 393 418861… 42 24.8 confin…
#> 7 28.9 16.3 1993 93242c… 393 418861… 42 24.8 confin…
#> 8 37.5 15.9 1993 93242c… 393 418861… 40 21.3 confin…
#> 9 35.1 24.4 1993 93242c… 393 418861… 40 21.3 confin…
#> 10 30.4 20.7 1993 93242c… 393 418861… 119 28.5 confin…
#> # … with 5,034 more rows, 17 more variables: W_static.sd <dbl>,
#> # surface_water.distance <fct>, n_rehab <int>, time_since_rehab_years <dbl>,
#> # volume_m3_d.mean <dbl>, volume_m3_d.cv <dbl>, quality.EC <dbl>,
#> # quality.DO <dbl>, quality.Temp <dbl>, quality.pH <dbl>,
#> # quality.Redox <dbl>, quality.Fe_tot <dbl>, quality.Mn <dbl>,
#> # quality.NO3 <dbl>, quality.PO4 <dbl>, quality.SO4 <dbl>, quality.TSS <dbl>,
#> # and abbreviated variable names ¹construction_year, ²screen_material, …
tibble::as_tibble(df_test)
#> # A tibble: 1,264 × 26
#> Qs_rel well_age_years const…¹ scree…² diame…³ drill…⁴ admis…⁵ opera…⁶ aquif…⁷
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <fct> <dbl> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <fct>
#> 1 97.8 23.2 1970 5bad81… 300 418861… 176 39.1 confin…
#> 2 78.5 29.5 1970 5bad81… 300 418861… 176 39.1 confin…
#> 3 52.2 35.0 1970 5bad81… 300 418861… 176 39.1 confin…
#> 4 27.2 42.9 1970 5bad81… 300 418861… 176 39.1 confin…
#> 5 35.1 20.9 1993 93242c… 393 418861… 93.5 44.7 unconf…
#> 6 82.7 6.07 1993 93242c… 393 418861… 42 24.8 confin…
#> 7 26.8 20.9 1993 93242c… 393 418861… 40 21.3 confin…
#> 8 16.9 24.4 1993 93242c… 393 418861… 40 21.3 confin…
#> 9 56.1 16.5 1993 93242c… 393 418861… 119 28.5 confin…
#> 10 68.5 6.11 1993 93242c… 393 418861… 75 33.5 edges …
#> # … with 1,254 more rows, 17 more variables: W_static.sd <dbl>,
#> # surface_water.distance <fct>, n_rehab <int>, time_since_rehab_years <dbl>,
#> # volume_m3_d.mean <dbl>, volume_m3_d.cv <dbl>, quality.EC <dbl>,
#> # quality.DO <dbl>, quality.Temp <dbl>, quality.pH <dbl>,
#> # quality.Redox <dbl>, quality.Fe_tot <dbl>, quality.Mn <dbl>,
#> # quality.NO3 <dbl>, quality.PO4 <dbl>, quality.SO4 <dbl>, quality.TSS <dbl>,
#> # and abbreviated variable names ¹construction_year, ²screen_material, …Regression
Hyperparameter Tuning
# Hyperparameter tuning --------------------------------------------------------
# specify model
xgb_model <- parsnip::boost_tree(
trees = 500,
tree_depth = tune::tune(), ## model complexity
min_n = tune::tune(), ## model complexity
loss_reduction = tune::tune(), ## model complexity
sample_size = tune::tune(), ## randomness
mtry = tune::tune(), ## randomness
learn_rate = tune::tune(), ## step size
) %>%
parsnip::set_engine("xgboost") %>%
parsnip::set_mode("regression")
# set up workflow
xgb_wf <- workflows::workflow() %>%
workflows::add_formula(Qs_rel ~ .) %>%
workflows::add_model(xgb_model)
# hyperparameter sampling v1
# xgb_grid <- dials::grid_random(dials::tree_depth(),
# dials::min_n(),
# dials::loss_reduction(),
# sample_size = dials::sample_prop(),
# dials::finalize(dials::mtry(), df_training),
# dials::learn_rate(range = c(0.01, 0.1),
# trans = NULL),
# size = 1000)
# hyperparameter sampling v2
xgb_grid <- dials::grid_latin_hypercube(
dials::tree_depth(),
dials::min_n(),
dials::loss_reduction(),
sample_size = dials::sample_prop(),
dials::finalize(dials::mtry(), df_training),
dials::learn_rate(),
size = 500
)
# define cross validation procedure
cv_folds <- rsample::vfold_cv(df_training, v = 5)
# set up random grid with 20 combinations for first screening
doParallel::registerDoParallel()
# test different hyperparameters via cross validation on training data
set.seed(234)
xgb_tuning <- tune::tune_grid(
xgb_wf,
resamples = cv_folds,
grid = xgb_grid,
control = tune::control_grid(save_pred = TRUE)
)
# get assessment metrics
metrics <- tune::collect_metrics(xgb_tuning)
dwc.wells::save_data(metrics,
path = getwd(),
filename = "metrics_tuning_xgb_random_resampling")
# visualise results
metrics %>%
#filter(learn_rate > 0.01) %>%
dplyr::filter(.metric == "rmse") %>%
dplyr::select(mean, min_n, mtry, tree_depth, learn_rate, loss_reduction, sample_size) %>%
tidyr::pivot_longer(c(min_n, mtry, tree_depth, learn_rate, loss_reduction, sample_size),
values_to = "value",
names_to = "parameter") %>%
ggplot2::ggplot(ggplot2::aes(value, mean, color = parameter)) +
ggplot2::geom_point(show.legend = FALSE, size = 0.5) +
ggplot2::facet_wrap(~parameter, scales = "free") +
ggplot2::labs(x = NULL, y = "RMSE [%]") +
sema.berlin.utils::my_theme()
ggplot2::ggsave("xgb_regression_hyperparameter_tuning_plot_random_resampling_1000_v2.png",
width = 8,
height = 4,
dpi = 600)
# after example from https://juliasilge.com/blog/xgboost-tune-volleyball/
}Best-Fit Model
# Specify model ----------------------------------------------------------------
xgb_model <- parsnip::boost_tree(mtry = 6,
min_n = 10,
trees = 500,
tree_depth = 7,
loss_reduction = 10,
learn_rate = 0.1,
sample_size = 0.7) %>%
parsnip::set_engine("xgboost",
nthreads = parallel::detectCores()) %>%
parsnip::set_mode("regression")
# Model training and assessment (regression) -----------------------------------
# Train model
set.seed(26)
xgb_fit <- xgb_model %>% parsnip::fit(Qs_rel ~ ., data = df_training)
#> [09:23:15] WARNING: amalgamation/../src/learner.cc:627:
#> Parameters: { "nthreads" } might not be used.
#>
#> This could be a false alarm, with some parameters getting used by language bindings but
#> then being mistakenly passed down to XGBoost core, or some parameter actually being used
#> but getting flagged wrongly here. Please open an issue if you find any such cases.
#usethis::use_data(xgb_fit, compress = "xz", overwrite = TRUE)
# Make predictions
predictions <- predict(xgb_fit, df_test)
# Evaluate model performance
df_pred <- df_test %>%
dplyr::select(Qs_rel) %>%
dplyr::bind_cols(predictions)
yardstick::rmse(df_pred, truth = Qs_rel, estimate = .pred)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 rmse standard 14.4
yardstick::rsq(df_pred, truth = Qs_rel, estimate = .pred)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 rsq standard 0.794
# scatter plot
dwc.wells::scatterplot(df_pred,
lines_80perc = FALSE,
alpha = 1,
pointsize = 0.9)
#> Warning: Removed 216 rows containing missing values (geom_point).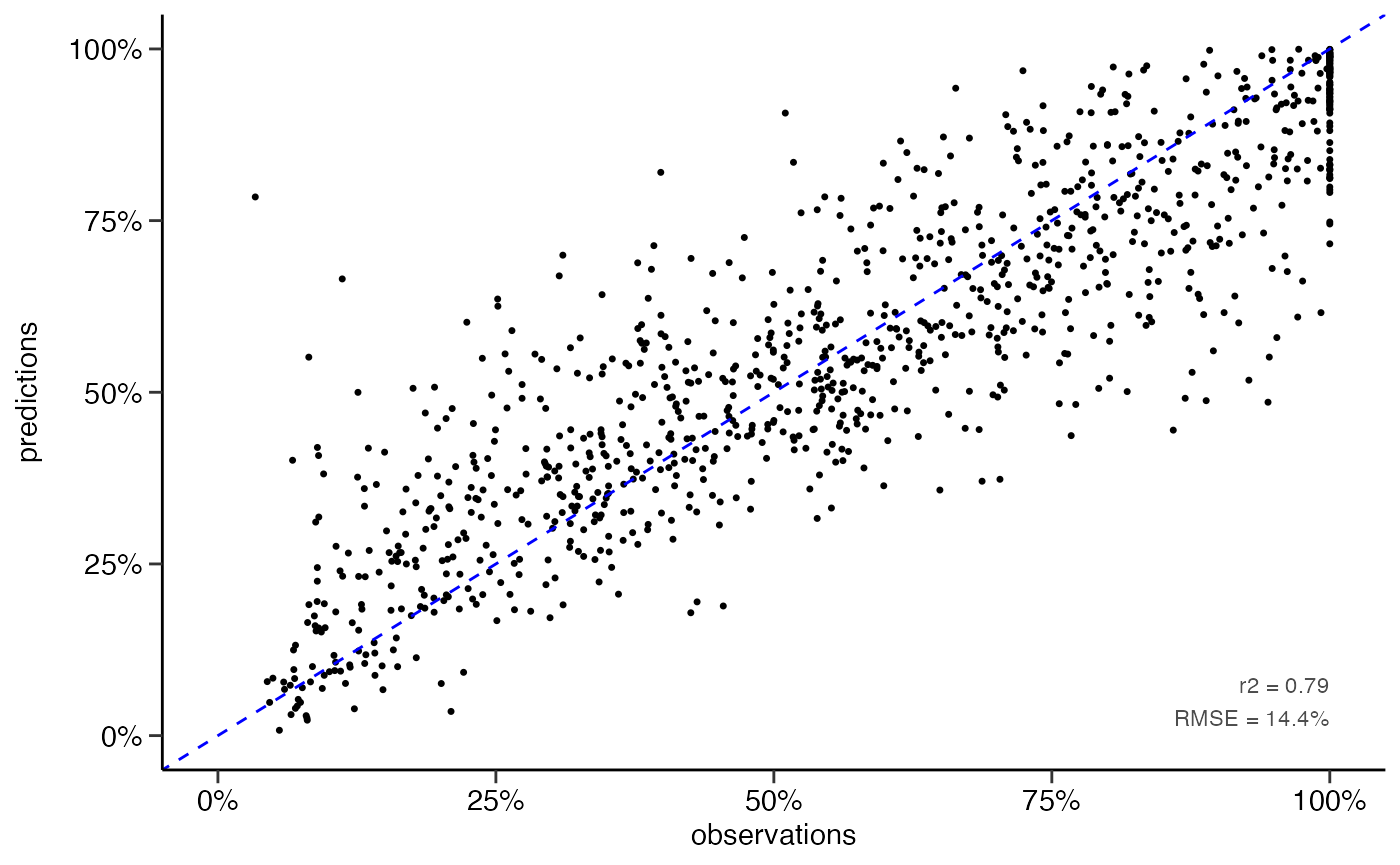
ggplot2::ggsave("scatterplot_xgb_numeric.png",
dpi = 600,
width = 3.5,
height = 3)
#> Warning: Removed 216 rows containing missing values (geom_point).Classification
# classification performance ---------------------------------------------------
# classify Qs data
df_pred <- df_pred %>%
dplyr::mutate(Qs_rel_class = dwc.wells::classify_Qs(Qs_rel),
.pred_class = dwc.wells::classify_Qs(.pred))
# confusion matrix
matrix <- yardstick::conf_mat(df_pred,
truth = Qs_rel_class,
estimate = .pred_class)
matrix
#> Truth
#> Prediction low high
#> low 725 99
#> high 45 395
# performance metrics
metrics <- summary(matrix)
metrics
#> # A tibble: 13 × 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 accuracy binary 0.886
#> 2 kap binary 0.756
#> 3 sens binary 0.942
#> 4 spec binary 0.800
#> 5 ppv binary 0.880
#> 6 npv binary 0.898
#> 7 mcc binary 0.759
#> 8 j_index binary 0.741
#> 9 bal_accuracy binary 0.871
#> 10 detection_prevalence binary 0.652
#> 11 precision binary 0.880
#> 12 recall binary 0.942
#> 13 f_meas binary 0.910
dwc.wells::save_data(matrix,
path = getwd(),
filename = "xgb_numeric_to_class_matrix_split80",
formats = "RData")